史上最大の絶滅
Worst mass extinction in earth history
顕生代(古生代〜現在)において生物は大量絶滅を5度経験したが(☞E4_2ページ)、中でもペルム紀末には史上最悪の絶滅事件が起きた。驚くべきことに種レベルで海洋生物の90%以上、陸上生物の70%以上が絶滅したのである。海では三葉虫や古生代型サンゴ、フズリナが完全に途絶え、ウミユリや海綿動物類、腕足類、貝類などの多くも深刻な打撃を受けた。陸では脊椎動物や昆虫、植物などの多くが絶滅した。一体、何が起きたのであろうか?
究極の原因は超大陸パンゲア(☞6ページ)にあった。パンゲアを形成する過程でコールドプルームが地球の深部へ沈み込んでいったが、その反動でスーパープルームと呼ばれる巨大なホットプルームがパンゲアにむかって上昇し、地表で規模の極めて大きな火山活動を引き起こした(図)。その結果、粘性の低い溶岩が洪水のように流れ出したが、その痕跡は中央シベリアの台地をおおう莫大な量の洪水玄武岩として現在でも確認することができる(図)。
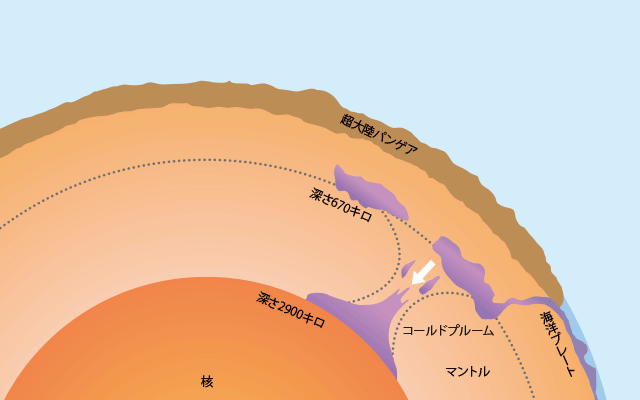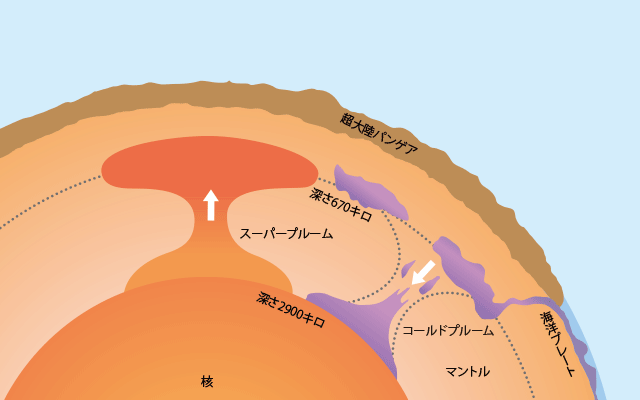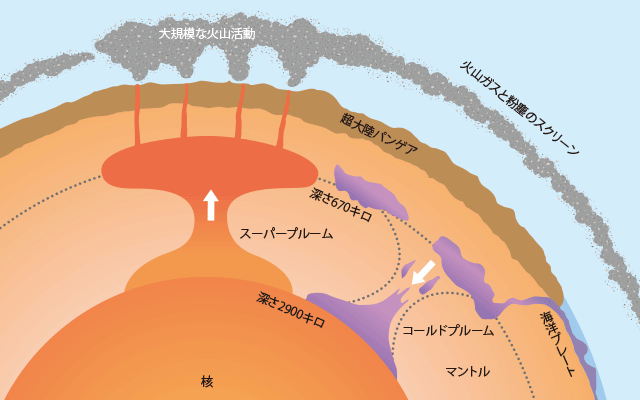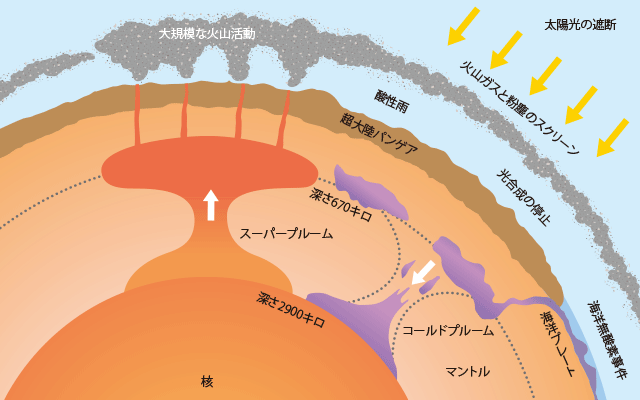
大規模な火山活動は温室効果ガスである二酸化炭素を大気中に大量に放出した。また、この温暖化によって海水の温度も上昇し、海底に大量に眠っていたメタンハイドレートを融解させた。メタンは二酸化炭素よりも強力な温室効果ガスであるので、メタンハイドレートの融解は、さらに温暖化を加速させた可能性がある。しかし、それだけではない。火山活動によって大気中に大量に放出された火山灰やエアロゾルは、太陽光をさえぎることで海の藻類や陸の植物の光合成を妨げて絶滅に追いやった。その結果、海洋で酸素が極端に少なくなる海洋無酸素事件が起こり、海洋動物の大絶滅を引き起こした。さらに、藻類や植物を餌とする生態系の崩壊によって絶滅が加速したことは、言うまでもないであろう。まさに負の連鎖である。
近年、ペルム紀末の大量絶滅は二段階に分かれた複合事件であったことが分かってきた。一度目の絶滅で破壊された生態系が回復する前に二度目の絶滅が起きたので、史上最悪の事件を招いたのである。いずれにせよ、ペルム紀末の大量絶滅によってそれまで栄えていた古生代型生物は衰退し、現代型生物が台頭することになった(☞E4_2ページ)。もし、この大量絶滅が起こらなければ、 その後、恐竜や人類が一時代を築くことはなかったかもしれない。
During the Proterozoic (from the Paleozoic to present days), living creatures experienced 5 mass extinctions (☞ E 4 _ 2), however the worst mass extinction event in all Earth history occurred at the end of the Permian. More than 90% of the marine species and more than 70% of the terrestrial organisms died out during this event.
In the sea, trilobites, fusulina and Paleozoic corals disappeared completely while sea lily, sponges, brachiopods, and shellfish among others were seriously hit. On land, many vertebrate animals, insects and plants went extinct. But what happened on Earth at this time?
The main cause of this mass extinction event was the supercontinent Pangea itself (☞ page 6). During the process of formation of the supercontinent Pangea, a cold plume sunk deeply into the earth and in reaction a huge hot plume called super plume raised, causing an extremely large volcanic activity on Pangea's surface (Figure). As a result, low viscosity lava flowed out like a flood, and its traces can still be confirmed as an enormous amount of flood basalt is covering the central Siberian plateau (Figure).
This large-scale volcanic activity released a large amount of a greenhouse gas called carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. In addition to the increase of greenhouse gas, the seawater temperature rose due to the global warming which result in the melting of methane hydrate that slept in the ocean floor. As methane is a more potent greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide, melting of the methane hydrate may have further accelerated global warming. But that is not finished. Volcanic ashes and aerosols released in large quantities into the atmosphere by the volcanic activity blocked the sunlight, hindered sea algae and land plants photosynthesis, and finally killed them. As a result, an oceanic anoxic event occurred and caused a mass extinction among marine animals. An oceanic anoxic event is when large parts of the ocean are depleted in oxygen. It goes without to say that the mass extinction event has been accelerated by the disappearance of algae and plants and by the collapse of the ecosystems that fed on this flora. It is a vicious circle. In recent years, it has been found that the mass extinction that occurred at the end of the Permian period is a complex case that is divided in 2 stages. In fact when the second mass extinction occurred, the ecosystems destroyed by the first extinction did not recovered yet. This led to the worst case in Earth history. In any case, the Paleozoic creatures that flourished until the Permian mass extinction have declined and a more modern type of life arose (☞ E 4 _ 2). If this mass extinction did not occur, then dinosaurs and mankind might not have been able to have their chance.